CWOI 线段树选做(22Dec)
Vjudge 线段树小专题ψ(`∇´)ψ
A - Circular RMQψ(`∇´)ψ
在环上做区间加区间最值。
\(1\le n \le 10^6\)。
就拆一下就行了,没啥好说的
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 | |
B - Buy Ticketsψ(`∇´)ψ
有 \(n\) 个人和一个初始为空的队列,每个人都被分配了一个数值,并且第 \(i\) 个人会插队到第 \(pos_i\) 个人后面(\(pos_i = 0\) 意味着站到队头)。
求经过 \(n\) 次插队后整个队列的情况,\(1\le n \le 2\times 10^5\)。
好久以前就见过这题了,只是当时没有做出来。
正着做很难搞,怎么做都是 \(O(n^2)\) 的,考虑类似 ARC080E Young Maids 那题的思路,倒过来观察合法解的形状。
发现如果一个人是最后插队的,那么他的位置一定是固定的,类似地往前走就能确定每一个人的位置。
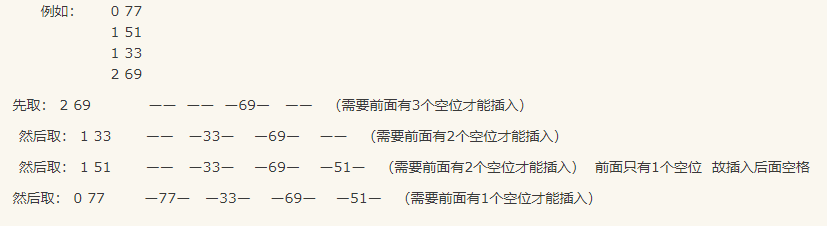
具体来说,我们维护 \([1, n]\) 的区间“空位”个数和,然后倒序插入,过程类似这个(图源https://www.cnblogs.com/zhengguiping--9876/p/4717024.html):
于是线段树二分一下就能解决了。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 | |
POJ 神笔玩意儿卡 cin,记得用 scanf。
C - Who Gets the Most Candies?ψ(`∇´)ψ
Statement
N children are sitting in a circle to play a game.
The children are numbered from 1 to N in clockwise order. Each of them has a card with a non-zero integer on it in his/her hand. The game starts from the K-th child, who tells all the others the integer on his card and jumps out of the circle. The integer on his card tells the next child to jump out. Let A denote the integer. If A is positive, the next child will be the A-th child to the left. If A is negative, the next child will be the (−A)-th child to the right.
The game lasts until all children have jumped out of the circle. During the game, the p-th child jumping out will get F(p) candies where F(p) is the number of positive integers that perfectly divide p. Who gets the most candies?
Input There are several test cases in the input. Each test case starts with two integers N (0 < N ≤ 500,000) and K (1 ≤ K ≤ N) on the first line. The next N lines contains the names of the children (consisting of at most 10 letters) and the integers (non-zero with magnitudes within 108) on their cards in increasing order of the children’s numbers, a name and an integer separated by a single space in a line with no leading or trailing spaces. Output Output one line for each test case containing the name of the luckiest child and the number of candies he/she gets. If ties occur, always choose the child who jumps out of the circle first.
就是一个约瑟夫环的问题,想法类似 B 题,就是维护空位之类的东西然后线段树二分。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 | |
D - Fast Matrix Operationsψ(`∇´)ψ
有一个 \(r\) 行 \(c\) 列的全 \(0\) 矩阵,有以下三种操作。
1 X1 Y1 X2 Y2 v将子矩阵 \((X1,Y1,X2,Y2)\) 的元素加 \(v,(v > 0)\)。
2 X1 Y1 X2 Y2 v将子矩阵 \((X1,Y1,X2,Y2)\) 的所有元素变为 \(v\)。
3 X1 Y1 X2 Y2查询子矩阵 \((X1,Y1,X2,Y2)\) 的和,最大值,最小值。输入保证和不超过 \(10^9\),矩阵不超过 \(20\) 行,矩阵元素个数不超过 \(10^6\)。
翻译来自 Luogu-@Himself65。
发现矩阵不超过 \(20\) 行,所以可以直接暴力对每一行维护。
然后我们就只需要区间加区间修改区间求和区间最值。
注意到区间加和区间修改都是需要 lazytag 的,我们思考一下 lazytag 的顺序。
这里为了方便就懒得用群论的语言解释了。
可以发现,如果一个节点被先打上一个 add 标记,然后打上一个 set 标记,add 标记会被直接覆盖。
如果先打上一个 set 标记,后打上一个 add 标记,是没有任何影响的。
所以在 pushdown 的时候我们需要先处理 set,在区间修改和下放 set 标记的时候要注意清空 add 标记。
就这样,只是比较难写,然后修改的 \(v\) 好像没有限制,所以保险起见我们用一个值域外的数表示空标记就行了。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 | |
还有一个点是,直接开 \(21\) 个线段树会炸,所以我们需要用 new/delete 动态创建数组。
这个题好像说是有多测,但是数据可能是用脚造的,所以我忘记取消注释了也都没有事情,也有可能是我读错了。
E - Paradeψ(`∇´)ψ
题意和题解看这里的复盘报告。
F - Help with Intervalsψ(`∇´)ψ
题意有点复杂,我直接粘贴原题面了:
Statement
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | |
首先考虑一个问题是,怎么处理开区间和闭区间。
这个比较简单,我们把每个点看作两个点,分别表示这个点作为开/闭区间端点的情况。
然后这样就很方便修改。
比如 \((1, 3]\) 就拆成 \((1), [2], (2), [3]\) 就行了。
转化回来的话,你发现开区间一定是奇数,闭区间一定是偶数,然后就行了。
于是现在要做的就是看这个操作怎么转化成比较方便操作的语言。
其实就是维护一堆 0/1,然后要支持一定的区间翻转和区间异或操作,只不过维护的时候可以直接只维护两个 tag,最后再暴力处理,毕竟只有 0/1 嘛。
U: 把区间 \([l,r]\) 覆盖成 \(1\)I: 把 \([-\infty,l), (r,\infty]\) 覆盖成 \(0\)D: 把区间 \([l,r]\) 覆盖成 \(0\)C: 把 \([-\infty,l), (r,∞]\) 覆盖成 \(0\), 且 \([l,r]\) 区间整体异或 \(1\)S: \([l,r]\) 区间整体异或 \(1\)
Cover 操作是 Trivial 的,Xor 只需要分割区间然后在区间上面打一个标记。
注意 Xor 不能覆盖 Cover 只能把 Xor 打到 Cover 身上,Cover 可以覆盖 Xor,就是一个优先级的问题。
嗯嗯,然后做完了。
Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 | |